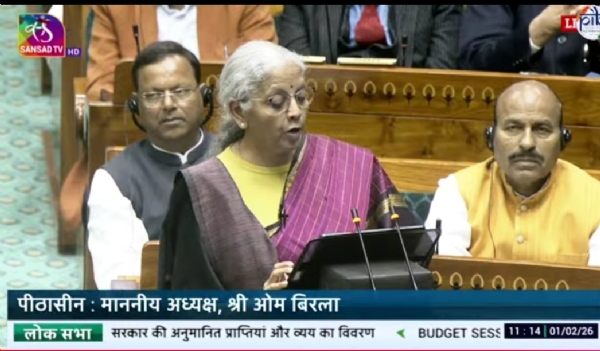
Kathmandu, 01 February (H.S.): India has reaffirmed its long-term development partnership with Nepal by provisioning ₹800 crore assistance for fiscal year 2026-27.This information appears in budget documents released by India's Ministry of External Affairs (MEA). Actual expenditure on Indian aid to Nepal in FY 2024-25 stood at ₹701.62 crore. FY 2025-26 budget estimate of ₹700 crore was subsequently revised upward to ₹830 crore.
The ₹800 crore allocation for 2026-27 reflects balanced strategic adjustment within India's regional policy rather than diminished priority for Nepal.
Under MEA's 'Aid to Countries' framework, Nepal ranks prominently alongside Bhutan, Sri Lanka, and Maldives as major aid recipients from India. Most Indian assistance to Nepal comprises grants, enabling Kathmandu to implement development projects without escalating external debt burdens.
Over years, this support has bolstered infrastructure including roads, bridges, electricity transmission lines, schools, hospitals, drinking water projects, and cultural heritage restoration.
A substantial portion of Indian aid traditionally targets high-impact community development projects and border area infrastructure, directly influencing local livelihoods and cross-border connectivity. Officials linked to bilateral cooperation indicate forthcoming fiscal year will prioritize energy connectivity, trade facilitation, and people-to-people contacts.
This assistance arrives as Nepal grapples with economic pressures, post-pandemic recovery challenges, and requirements for large-scale infrastructure investment. In this context, India's steady support emerges as a vital source of stability and predictability within Nepal's external development partnerships. From regional perspective, this sustained assistance aligns with India's 'Neighbourhood First' policy while underscoring Nepal's strategic importance in South Asia.
---------------
Hindusthan Samachar / Jun Sarkar